Gauss's Theorem and Its Applications
Gauss's Theorem and Its Applications: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Gauss Theorem in Electrostatics, Electric Field inside the Overlapping Region of Two Oppositely Charged Spheres & Electric Field inside the Cylindrical Cavity of Uniformly Charged Cylinder etc.
Important Questions on Gauss's Theorem and Its Applications
Which law is used to derive the expression for the electric field between two uniformly charged large parallel sheets with surface charge densities and respectively:
Applying Gauss theorem, the expression for the electric field intensity at a point due to an infinitely long, thin, uniformly charged straight wire is
A thin infinite sheet charge and an infinite line charge of respective charge densities and are placed parallel at distance from each other. Points and are at and perpendicular distances from line charge towards sheet charge, respectively. and are the magnitudes of resultant electric field intensities at point and respectively. If for then the value of is _____.
Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R.
Assertion A : If an electric dipole of dipole moment is enclosed by a closed surface, the net flux coming out of the surface will be zero.
Reason R : Electric dipole consists of two equal and opposite charges.
In the light of above, statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below.
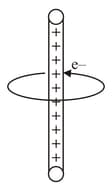
An electron revolves around an infinite cylindrical wire having uniform linear charge density in circular path under the influence of attractive electrostatic field as shown in the figure. The velocity of electron with which it is revolving is ______________ . Given mass of electron
Graphical variation of electric field due to a uniformly charged insulating solid sphere of radius with distance from the centre is represented by:
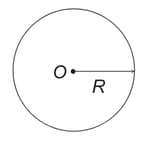
A charge is enclosed by a Gaussian spherical surface of radius . If the radius is doubled, then outward electric flux will
Two identical infinite negative line charges are held along the lines in the plane. A charge- is placed at origin & is restricted to move along axis.Its equilibrium is
If the charge given to an insulated sphere behaves as the whole charge is at the centre of sphere then the observation point is -
(1) outside the surface
(2) on the surface
(3) outside or on the surface
(4) at the centre
In a uniform electric field find the total flux associated with the given surfaces
For a closed surface the flux associated is . On adding to it, it becomes . Then initial charge enclosed by surface is :-
When two conducting spheres are placed at a distance from each other and connected with a wire then will sphere produce a field at the centre of sphere ?
At what distance from the centre of ring on axis, electric field is maximum :-
A positive charge q having mass , is released from rest in front of an infinite non-conducting sheet with surface charge density equal to . Speed of the charge particle after time is
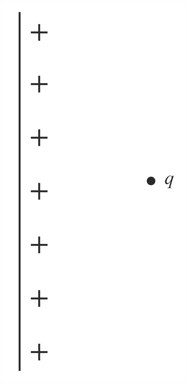
The flux passing through the curved surface of the frustum is as shown in the figure. If a charge is distance below the top, then:
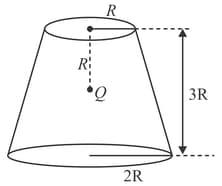
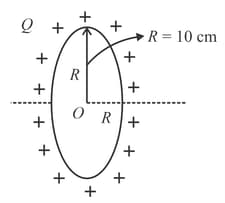
A charge is surrounded by a closed surface consisting of an inverted cone of height and base radius , and a hemisphere of radius as shown in the figure. The electric flux through the conical surface is (in units). The value of is _____ .
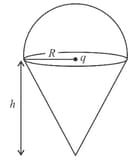
A sphere has a positive charge. Figure shows variation of electric field with distance from its centre. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
Is Gauss's law valid for the gravitational fields also?
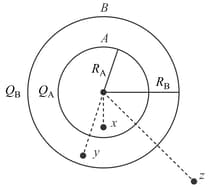
Consider an isolated, thin conducting spherical shell of radius . The shell is given a charge that distributes uniformly and due to only the maximum strength of the resulting electric field has a value due to only. is another isolated thin conducting spherical shell of radius . It is given a charge that distributes uniformly and in this case, maximum strength of the resulting field has a value due to only. The two shells and are now kept in a concentric manner as shown in figure. and are points as shown in figure, at distance from the centre, respectively. [Take at ]
State Gauss's law with diagrammatic representation.
